What is the Internet of Things?
The term “Internet of Things” (IoT) often brings to mind consumer-focused innovations like smart appliances, video doorbells, or wearable devices such as smartwatches. While these applications are widely recognized, they represent only a fraction of IoT’s potential. Beyond the consumer space, businesses, organizations, and researchers leverage IoT to gather critical data that informs usage patterns, optimizes resource management, and enables the creation of need-based schedules.
A key consideration for IoT applications is the ability of sensors to reliably transmit data. Factors such as radio frequency interference—caused by physical barriers like buildings or challenging geographical conditions—and the connectivity infrastructure play a vital role in ensuring successful data transmission. Common connectivity options include cellular networks and low-power wide area networks (LPWAN), both of which are widely used for IoT deployments. However, in remote areas where access to cellular towers or LPWAN gateways is limited, satellite connectivity becomes an essential solution for transmitting data effectively.
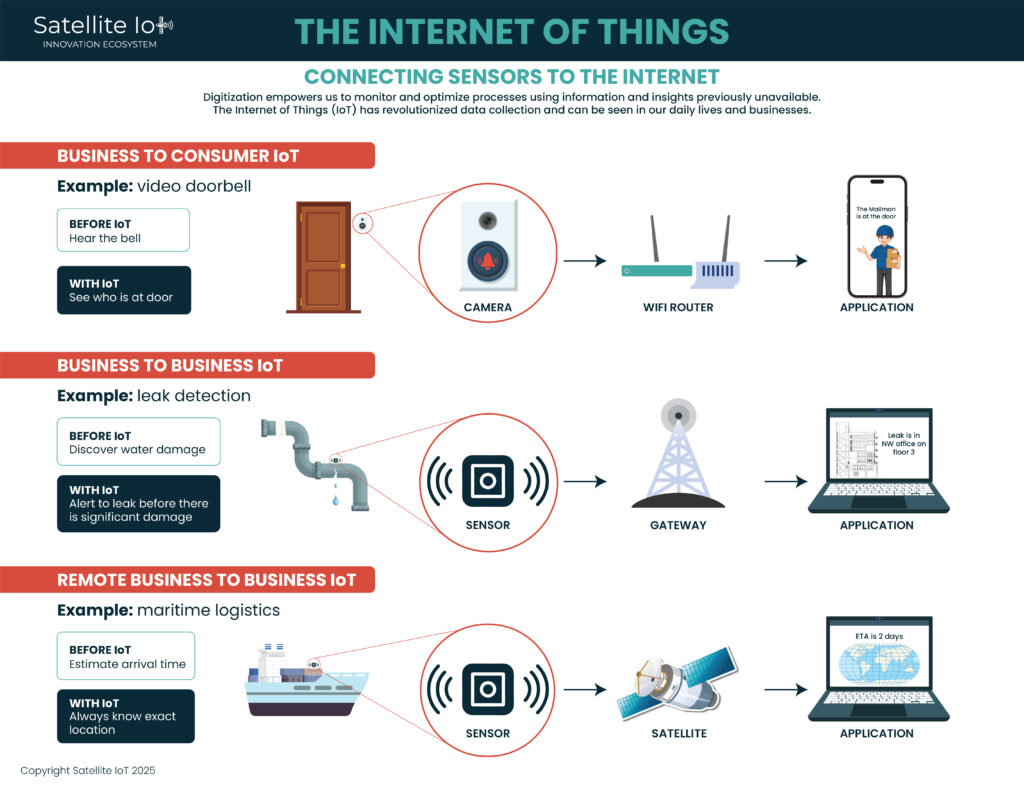
This infographic explains three different markets that can be addressed with IoT: B2C, B2B, and remote B2B.
What applications might use IoT?
Businesses, organizations, and researchers can all benefit from the efficient data collection made possible with IoT solutions. For example:
Agriculture: Smart Farming
IoT has revolutionized agriculture with smart farming solutions that optimize resources while increasing productivity:
-Precision Farming: Soil sensors measure moisture, temperature, pH levels, and nutrient content to determine the exact needs of crops, minimizing waste and maximizing yields.
– Automated Irrigation Systems: IoT-enabled systems schedule watering based on soil moisture levels and weather conditions to prevent over- or under-watering.
– Livestock Monitoring: GPS-enabled collars track the location and health of animals in real time.
– Smart Greenhouses: IoT sensors control temperature, humidity, and lighting automatically to create optimal growing conditions.
– Agricultural Drones: Drones equipped with cameras and sensors assess crop health from above, identifying pest infestations or nutrient deficiencies before they spread.
Environmental Monitoring
IoT supports sustainability efforts by tracking environmental conditions:
– Air and Water Quality Monitoring: Sensors measure pollutants to ensure compliance with regulations.
– Natural Resource Management: Soil moisture sensors optimize water usage in agriculture.
– Climate Data Collection: IoT networks gather large-scale environmental data to predict risks like flooding or droughts.
Logistics and Supply Chain Optimization
IoT enhances visibility and efficiency across supply chains:
– Real-Time Shipment Tracking: Sensors monitor shipment location and conditions, ensuring timely deliveries and reducing losses due to spoilage. For example, temperature sensors in shipping containers help maintain optimal conditions for perishable goods.
– Fleet Management: IoT devices optimize delivery routes by analyzing traffic and weather conditions, saving fuel and time.
– Cold Chain Monitoring: IoT-enabled systems ensure consistent refrigeration during transport, reducing waste in industries like food and pharmaceuticals.
Energy Infrastructure Management
IoT improves energy efficiency and reliability:
– Smart Grids: Utilities use IoT to monitor electricity demand in real time, balancing supply and demand effectively.
– Predictive Maintenance: Sensors detect anomalies in equipment like turbines or transformers to prevent costly failures.
– Energy Consumption Optimization: Smart meters analyze usage patterns to reduce waste and lower costs.
Predictive Analytics for Maintenance
IoT enables predictive maintenance across industries by collecting sensor data to forecast equipment failures:
– In logistics, vehicle sensors predict maintenance needs before breakdowns occur.
– In agriculture, predictive analytics help farmers plan irrigation schedules based on weather patterns and soil conditions.
Benefits of Implementing IoT
Operational Efficiency: Streamlined processes reduce manual intervention.
Cost Savings: Predictive maintenance lowers operational expenses.
Sustainability Goals: Environmental monitoring aligns operations with eco-friendly practices.
Enhanced Decision-Making: Real-time analytics enable proactive responses to challenges.
Businesses, organizations, and researchers should consider adopting IoT solutions to streamline data collection and analysis processes to unlock new opportunities for innovation.