Globally, river pollution is an escalating environmental stress, driven by urbanization, industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and insufficient wastewater treatment. Major rivers such as the Ganges in India, the Yangtze in China, the Danube in Europe, and the Mississippi in the USA face significant pollution loads, impacting biodiversity, drinking water sources, and public health. Contaminants like heavy metals, excess nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus), plastics, and pathogens are common threats. Despite regulatory frameworks such as the EU Water Framework Directive and the US Clean Water Act, enforcement and continuous assessment remain challenging, especially in remote or developing regions.
To address this, IoT (Internet of Things) monitoring systems have emerged as a transformative solution. By deploying networks of smart, interconnected sensors in rivers and watersheds, parameters like pH, dissolved oxygen, turbidity, and pollutant levels can be collected and transmitted to cloud platforms for analysis. Increasingly, satellite IoT (SatIoT) is playing a crucial role in extending connectivity to remote or infrastructure-poor areas, where traditional cellular networks are unavailable. Satellite constellations enable data transfer at low power from even the most inaccessible parts of river systems—supporting early detection of contamination, long-term trend analysis, and climate resilience planning. In Europe, projects like FIWARE and AQUASENSE integrate IoT with environmental compliance goals, while in the USA, EPA-funded initiatives pair IoT with GIS and remote sensing platforms to improve environmental governance.
River pollution sensors are essential for detecting various pollutants and assessing overall water quality. For river pollution monitoring, IoT systems typically integrate a core set of environmental sensors. Core sensors are generally the same due to global scientific standards, and with satellite ioT being very low power, deployments in remote locations can last on small battery power for years at a time. Though specific brands, certifications, and compliance standards may vary. With satellite IoT closing the connectivity gap, these technologies are now more accessible and scalable than ever, offering unprecedented visibility into freshwater health on a global scale.
- 🇪🇺 Europe
- Must often comply with EU Water Framework Directive (WFD).
- Common standards: ISO 5667, EN 27888, OIML.
- Typical vendors: Endress+Hauser, Hach (Europe branches), Sensorex, Libelium (Spain).
🇺🇸 USA: - Complies with EPA standards, Clean Water Act.
- Common standards: EPA 150.1, EPA 180.1, ASTM.
- Typical vendors: Campbell Scientific, YSI (Xylem), In-Situ, Hach (US-based).
Core IoT Sensors for River Pollution Monitoring
| Sensor Type | Purpose | Notes/Standards |
|---|---|---|
| pH Sensor | Measures acidity/basicity | Crucial for chemical balance |
| Turbidity Sensor | Detects water clarity (suspended particles) | Important for sediment pollution |
| Dissolved Oxygen (DO) | Measures oxygen levels in water | Indicator of aquatic life viability |
| Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) | Measures the amount of oxygen required for microbial decomposition of organic matter | Indicator of organic pollution levels |
| Temperature Sensor | Tracks water temperature | Affects DO and pollutant reactions |
| Electrical Conductivity | Indicates salinity or ion content | Correlates with pollution levels |
| Oxidation Reduction Potential (ORP) | Measures water’s ability to cleanse itself | Useful in detecting pollutants |
| Ammonia/Nitrate/Nitrite Sensors | Detects nutrient pollution | Critical for detecting agricultural runoff |
| Heavy Metal Sensors | Detects metals like lead, mercury, arsenic | Often electrochemical or optical |
| Hydrocarbon Sensor | Detects oil and petroleum-based pollutants | Vital near industrial zones |
| Flow Sensors | Measures water flow rate | Helps correlate pollution sources |
| Level Sensors | Monitors water height/volume | Useful for flood and contamination risk |
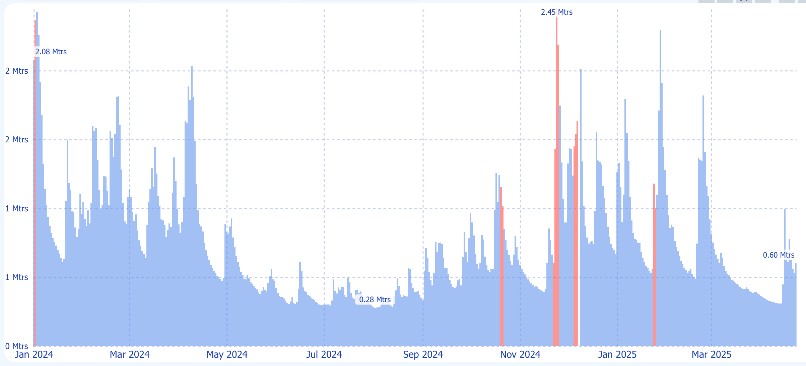
Satellite-Enabled Water Quality Monitoring in the Teifi River Valley
In a pioneering initiative to tackle water pollution in remote regions of West Wales, Lacuna Space partnered with ClearWater and Ceredigion County Council to deploy satellite-connected water quality sensors throughout the 122km Teifi River catchment. This collaboration, part of the Teifi Nutrient Monitoring (TNM) project, leverages Lacuna’s Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite IoT technology to overcome connectivity challenges in areas lacking reliable cellular coverage.

Sadly the Teifi is in an unfavourable condition, and in 2021 it was reported that it was exceeding acceptable water quality targets for phosphorus. Recent research has indicated that salmonoid fish stocks are in rapid decline on the Teifi, with modelling predicting the species could be lost within the next ten years unless urgent action is taken. Data suggests that discharges from wastewater treatment works are having a significant impact on the river, as well as diffuse pollution from agriculture and forestry activities, and pollution from the area’s legacy of metal mining.
ClearWater’s high-frequency sensors, strategically installed along the Teifi and its tributaries, continuously collect critical data on nutrient levels—specifically nitrates and phosphates—as well as river height fluctuations. These sensors have demonstrated remarkable resilience, maintaining data transmission even during adverse weather conditions.
The real-time data feeds into an interactive dashboard managed by Ceredigion County Council, providing stakeholders with up-to-date insights into water quality. This information is vital for identifying pollution sources, informing nutrient management plans, and guiding environmental protection efforts across the region.
This initiative exemplifies how satellite IoT technology can facilitate environmental monitoring in hard-to-reach areas, offering a scalable model for similar projects worldwide.
Notable IoT Devices and Systems in the UK
1. Proteus Multiprobe
Developed by Proteus Instruments in collaboration with the University of Birmingham, this device provides real-time data on parameters like DO, BOD, and bacterial contamination. It offers continuous monitoring of water health and is suitable for various applications, including environmental and recreational water quality assessments.
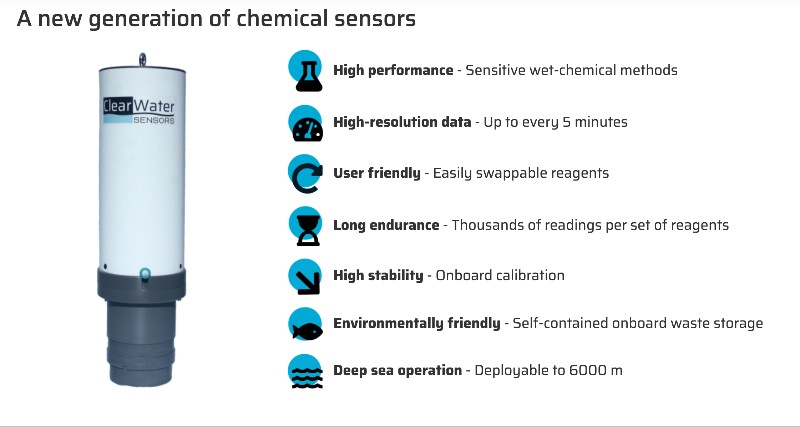
2. ClearWater Multi Sensor
Engineered by ClearWater Technologies, this modular sensor platform provides high-resolution data on water quality metrics including pH, turbidity, temperature, and conductivity. Designed for both surface and groundwater applications, it features adaptive calibration algorithms and supports LTE-M/NB-IoT connectivity for real-time remote monitoring. Its compact design makes it suitable for deployment in confined or hard-to-access aquatic environments.
3. EaMU River Level Sensors
Commissioned by the Environment Agency and developed by DefProc Engineering, these sensors monitor river levels across the UK. They utilize NB-IoT technology for low-power, long-range data transmission, making them ideal for remote locations.
4. ICT International’s IoT Water Quality Monitoring Station
This integrated solution uses LoRaWAN or CAT-M1/NB-IoT communication to monitor various water quality parameters. It includes sensors for pH, salinity, DO, and turbidity, and can be mounted on data buoys for anchored installations.
5. CSignum EM-2Q System
Designed for scenarios where real-time data is not required, this system logs water quality measurements at regular intervals. Data is retrieved on-demand using portable gateways, minimizing the need for permanent installations and reducing the risk of tampering.
6. Meteor Communications’ Water Quality as a Service (WQaaS)
Offering a subscription-based model, Meteor Communications provides real-time monitoring of water quality parameters using multi-parameter sondes. This service aids in identifying pollution events and supports proactive water management strategies.
Emerging Technologies and Initiatives
- AI-Powered Monitoring Systems: Companies like UnifAI Technology are developing AI-based systems that predict bacterial contamination levels using data from sensors measuring pH, temperature, turbidity, DO, and ammonia. These systems aim to provide real-time alerts to the public, enhancing safety for recreational water users.
- Scottish Water’s Smart Sewer Sensors: Trials are underway using IoT sensors to detect blockages and prevent pollution incidents in areas prone to flooding and sewage overflows.
Low-Cost Sensor Options
For broader deployment, especially in community-led monitoring projects, low-cost sensors are being explored:
- DFRobot Turbidity Sensor SEN0189: An affordable option for measuring water turbidity.
- Hanna Instruments HI98128: A portable pH and temperature tester suitable for field use.
- YSI EXO Series: Multiparameter sondes offering modular sensor options for various water quality parameters.
While these options are cost-effective, it’s essential to validate their accuracy against standard reference equipment to ensure reliable data.
Communication Technologies
Effective data transmission from sensors to monitoring centers is achieved using various communication technologies:
- LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network): Provides long-range communication with low power usage, ideal for dispersed sensor networks.
- NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT): Offers low power consumption and wide coverage, suitable for remote monitoring.
- CAT-M1: Supports higher data rates and mobility, beneficial for dynamic monitoring environments.
- Click here for a list of satellite IoT protocols.
These technologies ensure reliable and efficient data collection, even in challenging environments.